Derivation Of AR And Mr Curve Under Perfect Competition
-
- 0 Share
- 424 Views
Perfect Competition is a market structure where there is large number of buyer and seller with homogeneous goods selling at uniform(same) price.In perfect competition, firms refer to the profit-oriented organizations in the economy providing or producing broadly similar commodities or offering complementary services.
Industry is defines as group of firms and in perfect competition, firm is a price taker and price will be same.
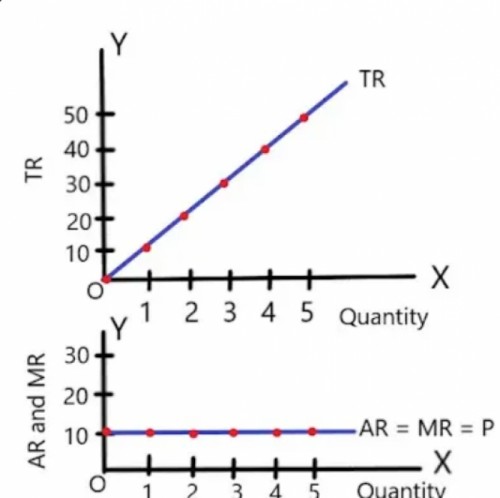
TABLE OF DERIVATION OF AR AND MR CURVE UNDER PERFECT COMPETITION:
| Q | P | TR | AR | MR |
| 0 | 5 | - | - | - |
| 1 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| 2 | 5 | 10 | 5 | 5 |
| 3 | 5 | 15 | 5 | 5 |
| 4 | 5 | 20 | 5 | 5 |
| 5 | 5 | 25 | 5 | 5 |
Where,
Q= No. of units sold
P=Price in Rs.
TR=P*Q
AR=TR/Q
MR=Change in TR/Change in quantity sold
In this table we can see that price is same. Since, AR and price are equal to each other. MR remains constant like AR because TR increase at same rate. Therefore, we can find that;
P=AR=MR
Please
